Why can’t I access this file?
Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
- Your membership has expired.
- The file is restricted to certain users.
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.

Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.



Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.

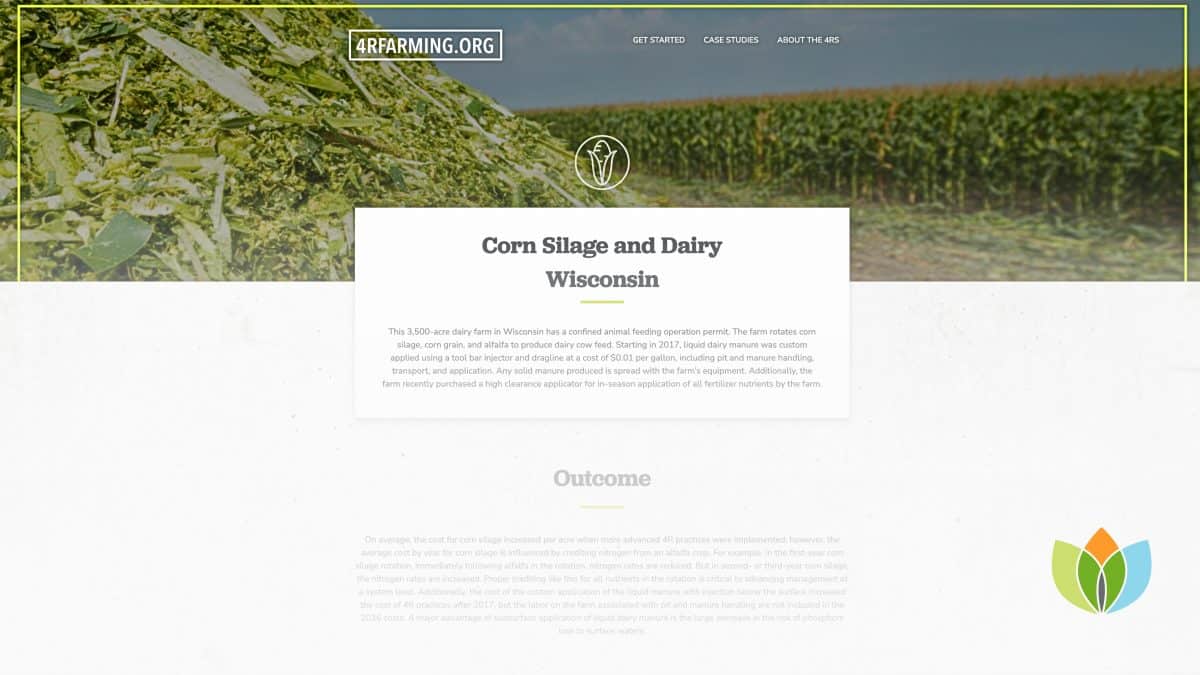
This 1,150 acre western Wisconsin farm operates a medium-size beef feedlot and grows in rotation alfalfa, corn silage, and corn grain. The solid beef pen pack manure is farmer applied to corn land. The farm also adds some liquid dairy manure that is custom applied to help meet crop nutrient needs. The remainder of the crop needs are applied in-season.
This farm with multi-year and crop rotation has a dynamic response in cost of practice change and nutrient use efficiency. Looking at corn silage production over three years, on average the farm decreased cost per acre as they transitioned to intermediate 4R practices. As the cost decreased on average, the nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen balance increased over time. This is happening for two reasons. One, the farm is doing an excellent job of crediting the nitrogen that is accumulated in the soil from the alfalfa portion of the rotation into their nitrogen applications. And two, beef manure is applied pre-plant supplying nitrogen to the early growing crop. These are strong practices for building soil health and organic matter.
The nitrogen balance is always negative with the corn silage years and lower in years where there is more first year corn silage. The rotation to alfalfa and the organic nitrogen from the residual beef manure that remains over time helps meet the nitrogen needs of the corn silage crop.
When the crop rotation is corn grain with alfalfa, the accounting for nitrogen from the alfalfa cost did go up as practices shifted to intermediate, but the lower cost in the first year corn is due to the lower fertilizer application from accounting for the nitrogen from the alfalfa crop.
In 2018, the farm transitioned from applying nitrogen pre-plant to an in-season side dress for nitrogen requirements and added software for managing records and weather impacts on nutrient applications. Through all years, the farm is crediting all nutrient sources and adjusting fertilizer needs based on the nutrient contributions from those sources.
| Year | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop | Corn Silage | Corn Silage | Corn Silage | Corn Silage |
| Cost ($/acre) | $249.10 | $208.03 | $165.80 | $92.70 |
| 4R Practice Level | Basic | Basic | Intermediate | Intermediate |
| Nitrogen Application Rate (lbs/ac) | 89 | 173 | 218 | 95 |
| Nitrogen Use Efficiency (lb N applied/bu of corn grain) | 2.9 | 5.2 | 6.6 | 3.8 |
| Nitrogen Balance (lb N applied – lb N harvested) | -181.4 | -115 | -69.9 | -123.3 |
| Phosphorus Application Rate (lbs/ac) | 60 | 73 | 53 | 40 |
| Yield (bu/ac) | 31 | 33 | 33 | 25 |
| Year | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop (Tons/acre) | Alfalfa Hay | Corn Grain | Corn Grain | Corn Grain |
| Cost ($/acre) | $137.86 | $108.55 | $172.53 | $154.21 |
| 4R Practice Level | Basic | Basic | Intermediate | Intermediate |
| Nitrogen Application Rate (lbs/ac) | 15 | 33 | 182 | 179 |
| Nitrogen Use Efficiency (lb N applied/bu of corn grain) | 3.33 | 0.20 | 1.01 | 1.19 |
| Nitrogen Balance (lb N applied – lb N harvested) | -89 | -93 | 49 | 68 |
| Phosphorus Application Rate (lbs/ac) | 30 | 73 | 73 | 60 |
| Yield (bu/ac) | 4.5 tons/ac | 170 | 180 | 150 |
Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.
Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.
Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.
Possible reasons you cannot access this file:
If you are seeing this message in error, please contact us.
This family farm located in central Illinois is managed by a young farmer who was an early adopter of the 4Rs. Seeing the benefits of these practices and willing to make investments in the farm, the family made advanced leaps in adoption of 4R practices and saw immediate returns.
When moving from basic to advanced 4R practices the total cost per acre to implement 4R practices decreased due to reduced fertilizer and equipment costs. Operation cost of an in-season sprayer and use of a smaller tractor for in-season nitrogen injection also lowered costs.
The time spent per acre implementing 4R practices was 0.21 hours per acre for basic practices compared to 0.22 with advanced practices, due to more fertilizer applications per season.
Changing from basic to more advanced 4R practices, the farmer decreased cost per acre between $16.49 and $25.31, while also decreasing CO2 equivalent greenhouse gas emissions by 34.7 percent.
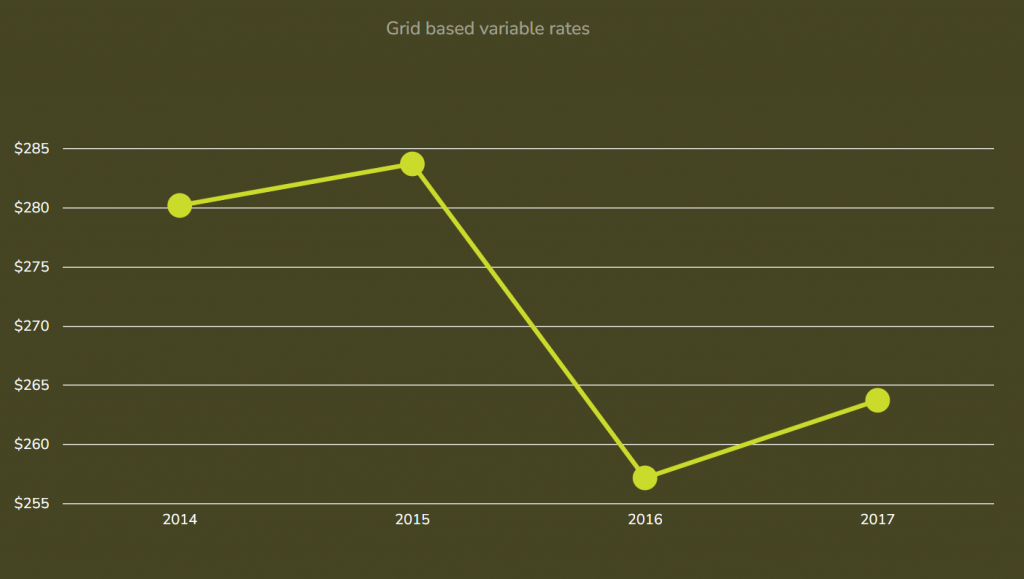
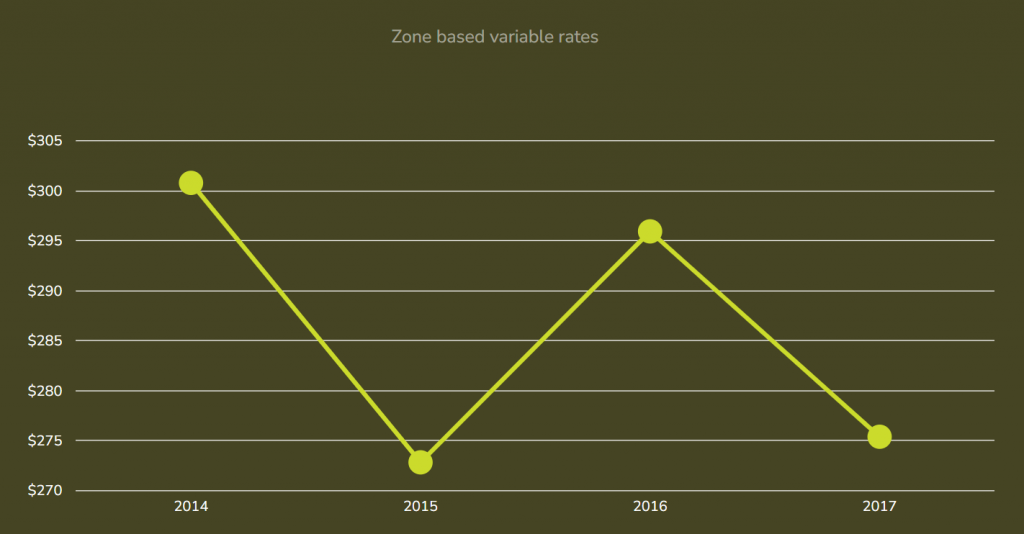
On all fields:
2014 – Basic
2015 – Basic
2016 – Intermediate
2017 – Advanced
| year | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4R Practice Level | Basic | Basic | Intermediate | Advanced |
| Nitrogen Application Rate (lbs/ac) | 253 | 208 | 253 | 204 |
| Nitrogen Use Efficiency (lb N applied/bu of corn grain) | 1.11 | .95 | 1.03 | 0.8 |
| Nitrogen Balance (lb N applied – lb N harvested) | 69.5 | 31.9 | 56.6 | -1.14 |
| CO2e Emissions per Bushel | 9.4 | 8.43 | 8.17 | 6.14 |
| CO2e Percent Reduction | – | 10.3 | 13.1 | 34.7 |
| Yield | 229 | 220 | 245 | 256 |